You are here
TPS – Transcranial Pulse Stimulation in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
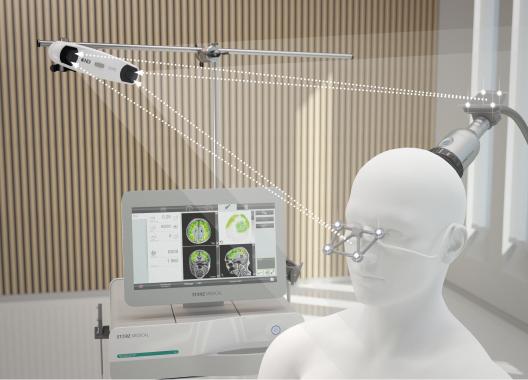
Neurolith System für die Behandlung von Alzheimer Patienten mit Transcranial Pulse Stimulation (TPS)
Transcranial Pulse Stimulation (TPS) is used in mild-to-moderate dementia in Alzheimer's disease to relieve symptoms, improve cognitive abilities, and slow the progression of the disease.
Low-intensity shock waves are delivered in a controlled manner to the affected regions of the patient's brain. There is an improvement in cerebral blood flow and the formation of new blood vessels. TPS induces the production of growth factors (BDNF, GDNF) in the brain, which lead to the regeneration of nerve cells. In this process, the formation of new nerve cells and their rewiring in the brain are promoted. Effects at the level of neurotransmitters can improve patients' mood. The procedure is painless, non-invasive and is performed while the patient is fully conscious.